Vertical Divider
People with High Flicker Sensitivity Bothered by OLED Displays
Recently, there has been a number of complaints about OLEDs operating at low luminance causing flickering. Flickering refers to the continuous alternating on and off of the screen. Physiologically, the eye responds to flicker, and the iris expands and contracts according to changes in brightness. This involuntary physiological reaction can explain the cause of headaches, especially after watching the screen for a long time. The eyes will feel tired because the eyes have been working hard. This is especially true when viewing the screen in a dark environment. People have varying reactions; some are not bothered by it while others claim to have telling physical affects.
Recently, there has been a number of complaints about OLEDs operating at low luminance causing flickering. Flickering refers to the continuous alternating on and off of the screen. Physiologically, the eye responds to flicker, and the iris expands and contracts according to changes in brightness. This involuntary physiological reaction can explain the cause of headaches, especially after watching the screen for a long time. The eyes will feel tired because the eyes have been working hard. This is especially true when viewing the screen in a dark environment. People have varying reactions; some are not bothered by it while others claim to have telling physical affects.
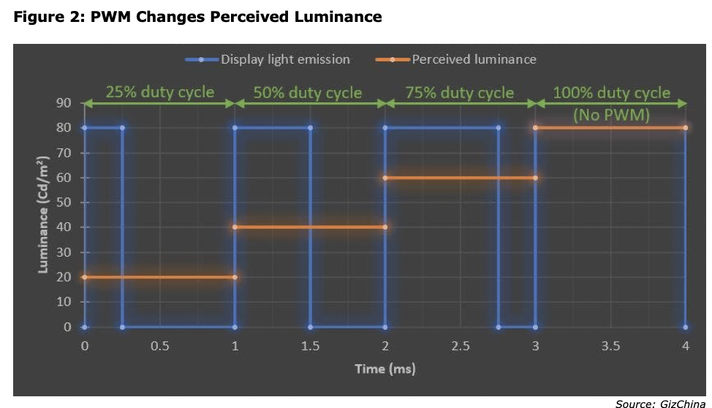
Smartphone screens flicker occurs on both LCD or OLED technology. LCDs and OLED panels use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to drive the panels with different pulse frequencies. However, people usually don’t see the LED switching between on/off (in other words flickering), only the screen dimming. The degree of dimming depends on the duration of the LED being off and on. The longer the off time, the darker the screen will look. Although LCD and OLED screens have different power supply methods for light sources, both technologies will have a flicker effect. However, the flicker effect of OLED screens is usually more pronounced than that of LCDs. First of all, the frequency range of OLED display and LCD display PWM is different. The PWM frequency range of the OLED screen is ~50~500 Hz, while LCD starts at around 1000 Hz or higher. Second, since the human eye is sensitive to flicker up to 250 Hz (at least for most people), OLED screens are more likely to cause eye fatigue than LCDs.
|
Contact Us
|
Barry Young
|