Vertical Divider
Nanosys Acquires μLED’ Display Developer glō
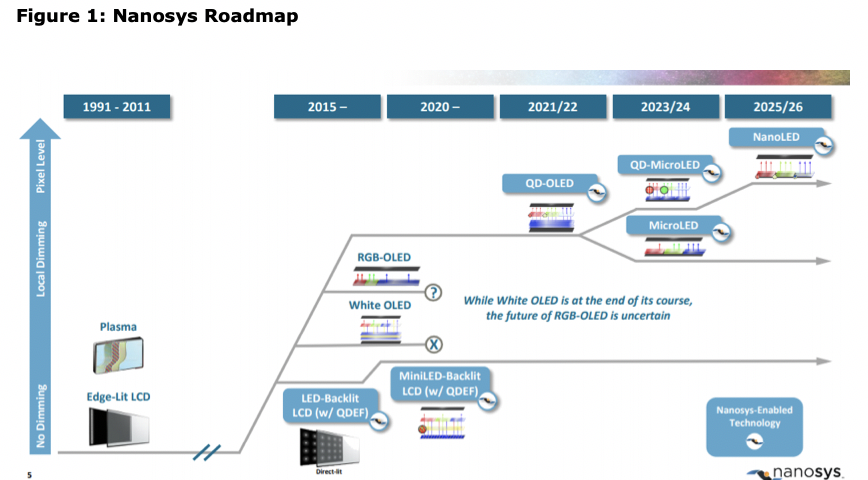
Glō’s contribution is efficient xGaN MicroLEDs based on proprietary methods and processes. The acquisition puts Nanosys’ is a position to develop MiniLED OLED, MicroLED and NanoLED display solutions. Prior to the acquisition, glō had invested over $200 million in its technology, which funded development of best-in-class MicroLED epitaxy, device and transfer technology, resulting in leading MicroLED performance at the smallest dimensions. But glō was unable to produce a commercial display product to sustain its high burn rate. The market currently lacks a cost effective MicroLED solution with ultra-small and bright pixels. Bringing MicroLED together with Quantum Dot could unlock the growth potential in this market.” The use of red and green QD color converters with blue Micro LEDs to create RGB displays. Of course, what’s still missing is a cost effective and high yield process to move the LEDs from the LED sapphire or carbon substrate to the display substrate. The use of QDs to convert blue LEDs, works for direct view displays, but not for micro displays, as the QD color converter configurations are not thin enough.
Glō’s contribution is efficient xGaN MicroLEDs based on proprietary methods and processes. The acquisition puts Nanosys’ is a position to develop MiniLED OLED, MicroLED and NanoLED display solutions. Prior to the acquisition, glō had invested over $200 million in its technology, which funded development of best-in-class MicroLED epitaxy, device and transfer technology, resulting in leading MicroLED performance at the smallest dimensions. But glō was unable to produce a commercial display product to sustain its high burn rate. The market currently lacks a cost effective MicroLED solution with ultra-small and bright pixels. Bringing MicroLED together with Quantum Dot could unlock the growth potential in this market.” The use of red and green QD color converters with blue Micro LEDs to create RGB displays. Of course, what’s still missing is a cost effective and high yield process to move the LEDs from the LED sapphire or carbon substrate to the display substrate. The use of QDs to convert blue LEDs, works for direct view displays, but not for micro displays, as the QD color converter configurations are not thin enough.
Jason Hartlove, Nanosys President & CEO, said “Combining the best Quantum Dot and MicroLED technologies allows Nanosys to unlock the disruptive potential of MicroLED by lowering production cost and maximizing performance.” The acquisition of glō expands Nanosys intellectual property portfolio enabling the company to continue to provide disruptive solutions to the massive $200 billion display market.
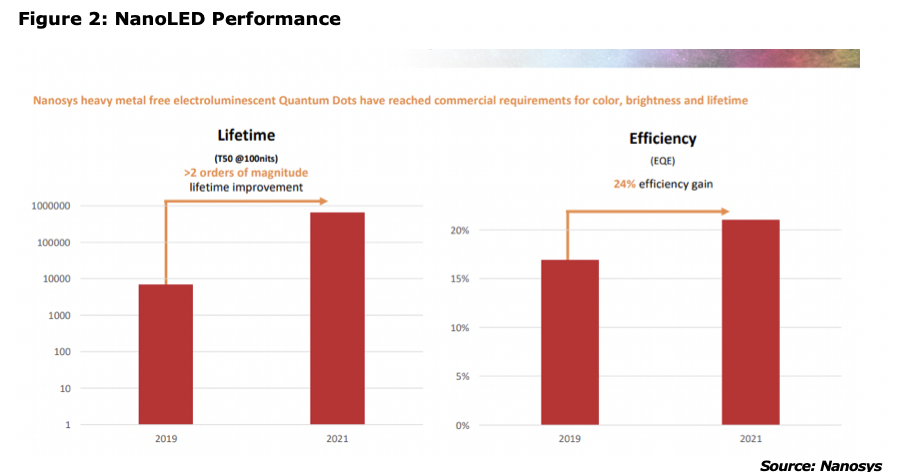
At DisplayWeek 2021, Jason presented the progress Nanosys has made in electroluminescent QDs, as shown in the next Figure. While the 2-order of magnitude improvement in lifetime is substantial, the nominal use of T50 and 100 nits is irrelevant when compared to commercial OLED lifetime, which has a performance measure of 30,000 hours at T97 and an initial luminance of 1400 nits for green.
At DisplayWeek 2021, Jason presented the progress Nanosys has made in electroluminescent QDs, as shown in the next Figure. While the 2-order of magnitude improvement in lifetime is substantial, the nominal use of T50 and 100 nits is irrelevant when compared to commercial OLED lifetime, which has a performance measure of 30,000 hours at T97 and an initial luminance of 1400 nits for green.
|
Contact Us
|
Barry Young
|