Vertical Divider
|
LCD TVs Change Light Guide Plate Material to Enable Thinner TV
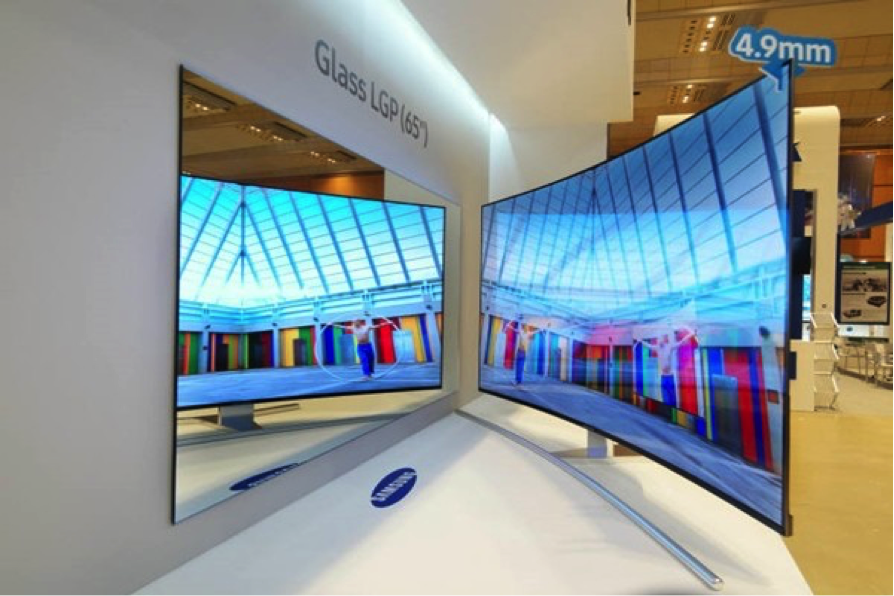
November,13 2017 One of OLED TV’s major selling points, in addition to FOS performance is the thinness of the device. LG’s Wallpaper OLED TV is 2.57mm thick and has been the talk of the industry. LCD TVs have been unable to compete on form factor because of the thickness of the light guide plate, which is a major part of backlight unit (BLU) for an edge lit LCD. The thickness of normal LCD TV is between 10mm and 15mm. Light-guide materials often use transparent poly methyl meth acrylate (PMMA). PMMA does not break easily due to its high solidity and is very light and has excellent transparency and gloss as it has the lowest light absorptiveness out of polymers within an area of visible ray. However it can be distorted or stretched as it is sensitive to heat and humidity. The width of the bezel can be widened and an air gap can be formed in order to prevent these problems. However these solutions thicken the BLU. Glass was recognized as a new light guide plate material as it can withstand heat and humidity really well. However it was not chosen due to its lower gloss. Display glass manufacturers changed composition of the glass and developed glass that is optimized for light guide plate’ characteristics. LG Display recently started mass-producing new LCD TV panels that use glass light guide plate instead of plastic, which drives the thickness down to 5mm. If the glass light guide plates are used for a LCD TV panel, its thickness could be reduced to 5mm. Figure 1: Samsung Display’s 65-inch Super-Slim Curved LCD w/Glass Light Guide Plate Source: Samsung
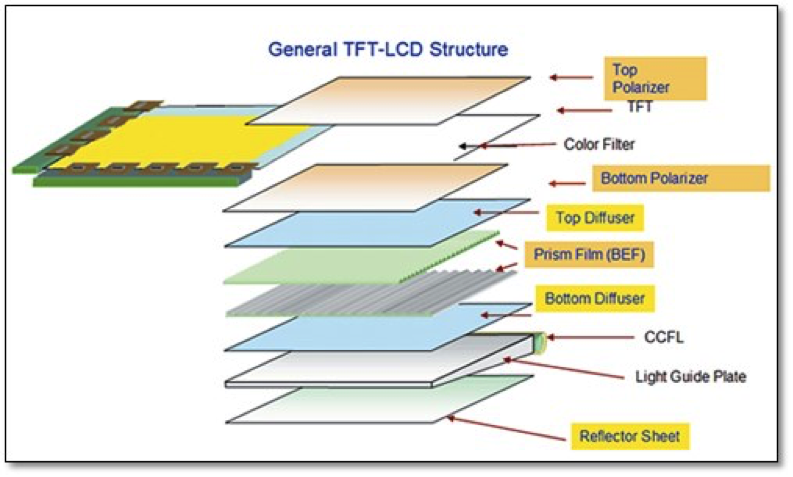
Asahi Glass developed a glass light guide plate ‘XCV’ which has 20 times the solidity of current light guide plate heat strain rate and expansion due to humidity that are 8 times and 100 times lower than current light guide plates. Asahi has been supplying the glass light guides to LG Display since July. Its is only 1.8mm thick, making it suitable for large TVs. LG Display is planning to mass-produce super-sized and ultra-thin LCD panels using Asahi Glass’ XCV, which will have almost zero bezel and will support an ultra-slim design. Corning also released a glass light guide plate called ‘Iris’ in 2015 and introduced 70-inch 4K LCD module prototype after partnering up with Japan’s SDP (Sakai Display Product). It claimed that using Iris can make ultra-thin LCD TV with less than 5mm of thickness. Samsung Display introduced a 65-inch UHD super-slim curved LCD panel prototype with thickness of 4.9mm by applying Corning’s Iris. Although it has yet to decide on a release date, it started promotions in the middle 2017 starting with China. In order to further reduce the thickness, Samsung Display coated QD material on top of the glass light guide plate instead of using QD film. However this method suffers from using a barrier film that protects QD material from heat and humidity. In order to overcome this limitation, Samsung Display is planning to introduce a product with better color representation power and brightness and lower thickness by integrating color filter and QD into one part. The issue of a QD color filter is the access to ambient light, which would distort the image if it gets to the QDs. Figure 2: General TFT LCD Structure Source: IHS
|
|
|
Contact Us
|
Barry Young
|